_____________________
Sol/Gel
Les hydrogels thermosensibles à base de poloxamères ont été développés en fort partenariat avec l’Ageps (V. Boudy) et la faculté de pharmacie (N. Mignet, J. Seguin, UTCBS) avec des collaborateurs hospitaliers de l’hôpital Lariboisière (Dr M. Pocard) et Ambroise Paré (Dr R. Malafosse). La conception de formulations gélifiantes mucoadhésives a été réalisée grâce à l’association de méthodes physico-chimiques (rhéologie) et de méthodes d’imagerie chez le petit animal afin de déterminer les durées de résidence des hydrogels et/ou principes actifs ou de déterminer des effets thérapeutiques. Nous avons ainsi pu montrer que nous pouvions prolonger la durée de vie d’API dans la muqueuse buccale de lapins (10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.09.073, Figure 1), que nous pouvions obtenir des effets adjuvants et néoadjuvants en délivrant des API cytotoxiques dans les tumeurs (10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.10.011, Figure 2), et plus récemment que nous pouvions stimuler la réponse immune in situ, conduisant à un effet abscopal (10.1080/2162402X.2018.1550342). Ces formulations ont été également optimisées pour la délivrance de principes actifs pour la voie oculaire conduisant à un produit pour la mydriase par la société Unither (10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118734 ; 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040360, Figure 3). Des formulations nanométriques, non cationiques, à cœur gélifié ont également permis d’encapsuler et délivrer des ARN interférants (10.3390/pharmaceutics13040479 ; 10.3390/pharmaceutics1304047).
Voie buccale :
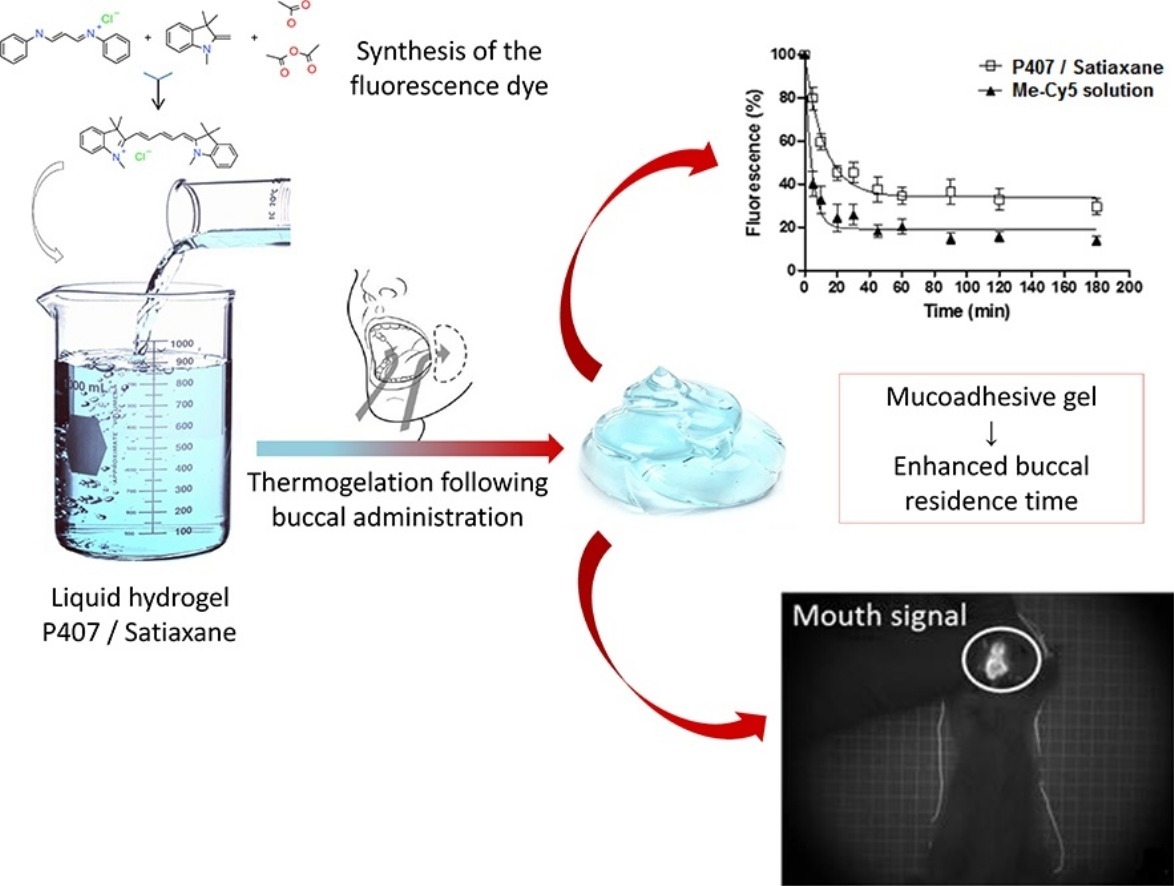
Fig. 1 : Validation in vitro et in vivo de gel thermosensibles pour l’administration buccale de médicament
Influence of additives on a thermosensitive hydrogel for buccal delivery of salbutamol: relation between micellization, gelation, mechanic and release properties 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.03.055
Poloxamer bioadhesive hydrogel for buccal drug delivery: Cytotoxicity and trans-epithelial permeability evaluations using TR146 human buccal epithelial cell line 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.09.045
Cyanine derivative as a suitable marker for thermosensitive in situ gelling delivery systems: In vitro and in vivo validation of a sustained buccal drug delivery 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.09.073
Application dans le cancer :

Fig.2 : Hydrogels thermosensibles pour l’administration locale de 5-fluorouracile en tant que thérapie néoadjuvante ou adjuvante dans le cancer colorectal
Local immunomodulation combined to radiofrequency ablation results in a complete cure of local and distant colorectal carcinoma ; 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1550342
Combination of tumor cell anti-adhesion and anti-tumor effect to prevent recurrence after cytoreductive surgery in a mice model ; 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.01.020
Thermosensitive hydrogels for local delivery of 5-fluorouracil as neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer ; 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.10.011
Voie oculaire :
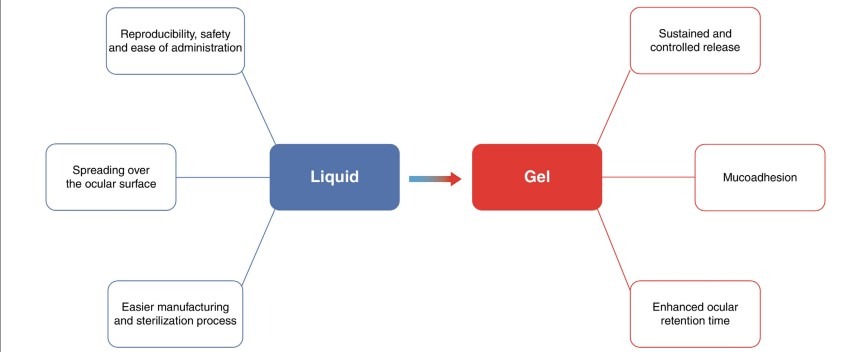
Fig. 3 : Avantages des phases liquide et gel des systèmes d’administration ophtalmique gélifiés in situ.
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of in situ gelling systems for sustained topical ophthalmic delivery: state of the art and beyond : 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.12.008
Novel in situ gelling ophthalmic drug delivery system based on gellan gum and hydroxyethylcellulose: Innovative rheological characterization, in vitro and in vivo evidence of a sustained precorneal retention time 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118734
In Situ Gelling Ophthalmic Drug Delivery System for the Optimization of Diagnostic and Preoperative Mydriasis: In Vitro Drug Release, Cytotoxicity and Mydriasis Pharmacodynamics 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040360
_____________________
À lire aussi

October 2025 – Thesis defense at UTCBS: Mitta PIERRE
On October 1st, 2025, Mitta PIERRE successfully defended her doctoral thesis entitled “Nanoformulations of antioxidant active ingredients for ophthalmic administration in the prevention of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)”
Sept 2025 – [Keynote recherche] Nathalie Mignet, Nanomédicaments et nanoparticules lipidiques pour la délivrance d’acide nucléique
La keynote de Nathalie Mignet, Directrice de l’UTCBS est en ligne!

Juillet 2025 – Workshop du master erasmus mundus Nanomed
Le workshop du master erasmus mundus Nanomed s est tenu à la faculté de pharmacie du 8 au 10 juillet.

Juin 2025 – Le congrès des Apprentis Chercheurs d’Université Paris Cité a eu lieu en juin dernier avec la participation de l’UTCBS
Le congrès des Apprentis Chercheurs d’Université Paris Cité a eu lieu en juin dernier avec la participation de l’UTCBS
